General pathology Details
General Pathology. Mobile Phone. HRTD 01797522136. General pathology is a complex and broad field. Pathology is a branch of medical science that studies diseases. It focuses on their causes, mechanisms, triggers, and patterns of change of cells or tissue and understanding how the body responds to and repairs injury.

There are many important topics in General Pathology. The topics are Atrophy, Hypertrophy, Metaplasia etc. General pathology is a common subject for all medical-related courses like the Paramedical Course, DMA Course, DMS Course, DMDS Course, Nursing Course, Dental Course, Pathology Course, Physiotherapy Course, etc. All these courses are available at HRTD Medical Institute.
Which topics are discussed in General Pathology?
- Cellular ageing
- Cellular response
- Cell death
- Apoptosis
- Necrosis
- Cellular adaptation
- Atrophy
- Hypertrophy
- Metaplasia
- Fatty changes
- Gangrene
- Cell injury
- Cellular changes
Cellular Aging in General Pathology
The process known as aging may occur due to continued damage to the cell or the expression of predetermined information within the genetic structure of the cell. Both processes lead to progressive cellular dysfunction which is evidenced by the organs of the body aging.
Cellular response
A cellular response is the response of a cell to extracellular signals. Cells, particularly cells in multicellular organisms, must be able to communicate and coordinate responses to maintain homeostasis in the body.
Cell death
Cell death can be defined as an “irreversible degeneration of vital cellular functions culminating in the loss of cellular integrity. There are 3 types of cell death.
- Type I cell death (apoptosis);
- Type II cell death (autophagy);
- Type III cell death (necrosis).
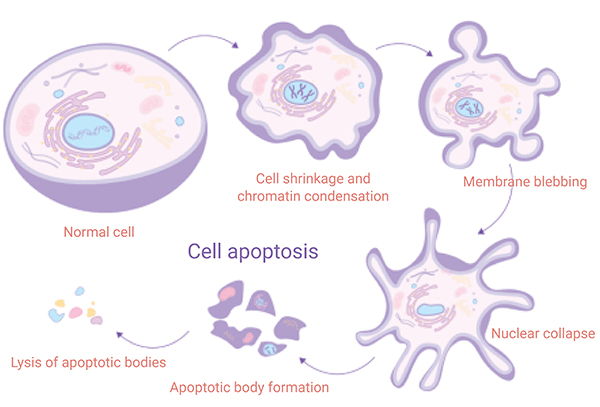
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a common topic of General Pathology. Apoptosis or programmed cell death is a type of cell death in which a series of molecular steps occur in a cell lead to its death. It occurs in controlled way.
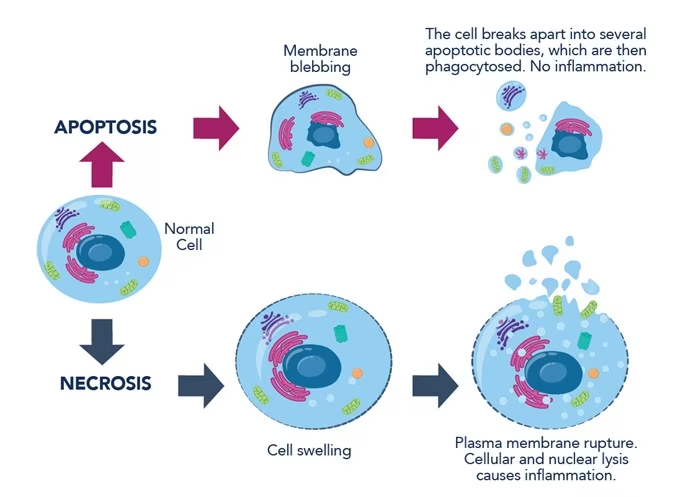
Necrosis
Necrosis is the process of unnatural or premature cell death that is triggered by disease or injury.
Autophagy
Autophagy is a protective process that breaks down aging or damaged cell parts so that they can be reused for cell repair or formation.
Cellular adaptation
Cellular adaptations refer to the changes made by cells in response to various stimuli or changes in their local environment. The four basic types of cellular adaptation .1. hyperplasia, 2.hypertrophy, 3.atrophy, and 4.metaplasia.
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia is an increase in the tissue or organ size due to increased cell number, without an increase in cell size. It can only occur in labile or stable cell populations. The cell proliferation in hyperplasia remains under physiological control and is reversible, unlike in neoplasia (cancer) which is irreversible.
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is an increase in the tissue or organ size due to an increase in cell size, without an increase in cell number. Hypertrophy usually occurs where there is increased functional demand on a tissue, or where there is hormonal stimulation.
Atrophy in General Pathology
Atrophy in General Pathology. Atrophy is the shrinkage of a tissue or organ due to a decrease in size and/or number of cells. It can occur physiologically, for example when the uterus decreases in size after birth following the cessation of production of hormones that stimulate its growth, or pathologically, for example, atrophy of an organ due to inadequate blood or nutritional supply.
Metaplasia
Metaplasia is the reversible change of one differentiated cell type to another. It usually occurs in epithelial tissues as an adaptive response to cell stress; cells can be substituted by those types better suited to the environment. This occurs via altered stem cell differentiation and thus metaplasia can only occur in labile or stable tissues.
Fatty Changes
Steatosis or fatty change, is abnormal accumulation of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver which is referred as fatty liver.
Gangrene
Gangrene is a one kind of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply or a serious bacterial infection. Gangrene is mainly 3 types .
- Dry Gangrene
- Wet Gangrene
- Gas Gangrene
Cell injury
Cell injury is a variety of changes of stress that a cell suffers due to external and internal environmental changes. cell injury is happened due to physical, chemical, infectious, biological, nutritional or immunological factors. Cell injury can be reversible or irreversible.
 Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh
Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh