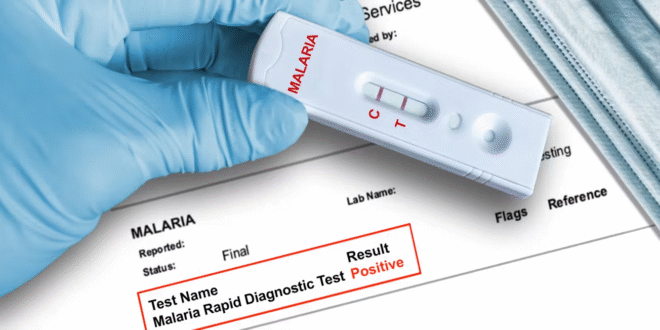
Malaria Test
Introduction
Malaria remains one of the most common and dangerous infectious diseases in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. It affects millions of people each year, particularly in Africa and South Asia. Bangladesh, being a tropical country, also experiences many cases of malaria, especially in rural and hilly regions. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to saving lives and preventing complications.
At HRTD Medical Institute, we believe that awareness and timely testing are the most powerful tools against malaria. This article aims to educate the general public about malaria testing—what it is, why it is important, how it is done, what the results mean, and how prevention and treatment can protect individuals and families.
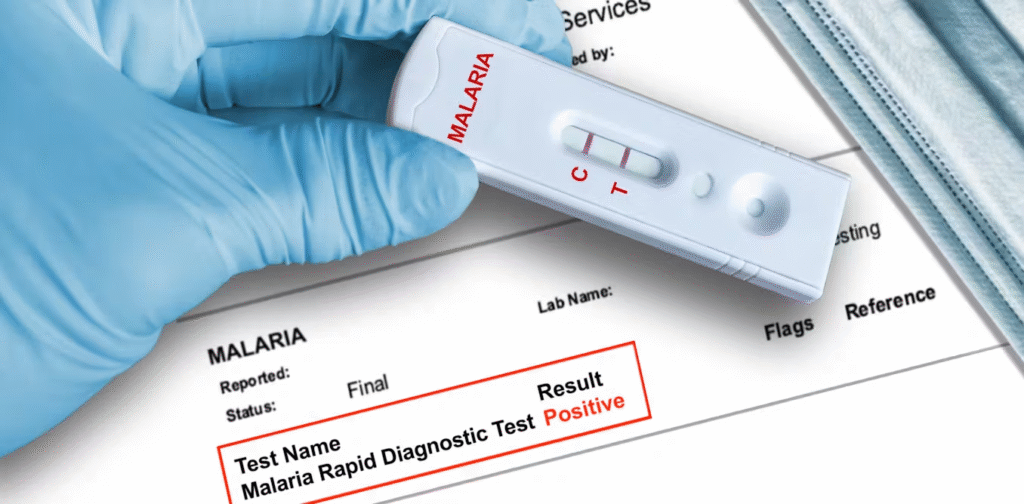
What Is Malaria?
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites of the genus Plasmodium. The infection is transmitted through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. When a mosquito carrying the malaria parasite bites a person, it injects the parasites into the bloodstream. These parasites then travel to the liver, where they mature and reproduce before infecting red blood cells.
There are several species of Plasmodium that infect humans:
- Plasmodium falciparum – the most dangerous and potentially fatal type.
- Plasmodium vivax – causes recurring malaria; common in Asia.
- Plasmodium malariae – causes milder infections but can last for years.
- Plasmodium ovale – rare and usually less severe.
- Plasmodium knowlesi – mainly found in Southeast Asia; can infect humans from monkeys.
Why Is Malaria Testing Important?
Malaria symptoms—such as fever, chills, and fatigue—can easily be mistaken for other common infections like dengue or viral fever. Therefore, accurate testing is essential to confirm whether malaria parasites are present in the blood.
Without testing, patients may receive the wrong treatment, leading to complications such as severe anemia, organ failure, or even death. At HRTD Medical Institute, our medical experts emphasize that malaria testing helps in:
- Early detection and treatment
- Preventing the spread of the disease
- Avoiding unnecessary medications
- Monitoring recovery and treatment response
When Should You Get a Malaria Test?
Anyone who has a high fever, shivering, sweating, and body ache, especially after visiting a malaria-prone area, should get tested. You should also consider testing if:
- You recently traveled to or live in areas with mosquitoes and stagnant water.
- You have recurring fevers at regular intervals.
- You are pregnant and live in an area where malaria is common.
- You experience symptoms that do not improve with regular fever medication.
At HRTD Medical Institute, we recommend testing as soon as symptoms appear—because early detection can save lives.
Types of Malaria Tests
There are several ways to diagnose malaria. The choice of test depends on the available facilities and the patient’s condition. Below are the main types of malaria tests:
1. Microscopic Blood Smear Examination
This is the gold standard for malaria diagnosis. A drop of blood is placed on a glass slide, stained with a dye (usually Giemsa stain), and then examined under a microscope by a trained technician.
The test can:
- Detect the presence of malaria parasites
- Identify the Plasmodium species
- Estimate the level of infection (parasite count)
At HRTD Medical Institute, we have advanced laboratory microscopes and trained laboratory technologists who carefully examine blood smears to provide accurate results.
2. Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs)
RDTs are quick, convenient, and suitable for field use. These tests detect specific malaria antigens (proteins) in the blood. A few drops of blood are placed on a test strip, and within 15–20 minutes, the result appears.
Advantages:
- No microscope required
- Results within minutes
- Useful in rural or emergency settings
However, RDTs may not detect very low levels of parasites and cannot always determine the species of Plasmodium. For confirmation, microscopy is still recommended.
HRTD Medical Institute provides both RDT and microscopic facilities for fast and reliable diagnosis.
3. Molecular Tests (PCR)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing is a highly sensitive method used in advanced laboratories. It detects parasite DNA, allowing for precise species identification even when the parasite count is very low.
Although expensive and time-consuming, PCR is valuable for research, complex cases, or when other tests are inconclusive.
At HRTD Medical Institute, PCR tests are part of our advanced diagnostic and research facilities used in collaboration with specialized laboratories.
4. Serological Tests
These tests detect antibodies produced by the immune system in response to malaria infection. However, they are mainly used for epidemiological studies rather than for diagnosing current infections.
Preparation Before a Malaria Test
No special preparation is usually required before a malaria test. However, it is important to:
- Inform your doctor about any medications you are taking.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Avoid taking antimalarial drugs before the test, as they may affect the results.
At HRTD Medical Institute, patients are guided step-by-step through the testing process to ensure comfort and accurate sample collection.
Sample Collection Process
A malaria test requires a small blood sample, usually taken from a vein (venipuncture) or a finger prick. The sample is then analyzed using the chosen testing method (microscopy, RDT, or PCR).
Our laboratory at HRTD Medical Institute follows all hygienic and safety standards during sample collection to ensure reliability and patient safety.
Understanding the Test Results
- Positive Result: Malaria parasites are found in the blood. The doctor will prescribe antimalarial medication depending on the species detected.
- Negative Result: No parasites are detected. However, if symptoms persist, the test may be repeated after a few hours or days.
- False Negative: In some cases, parasites may be too few to detect initially, so follow-up testing is important.
The experts at HRTD Medical Institute always review results carefully and may recommend follow-up tests if necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Symptoms of Malaria
Common symptoms include:
- High fever with chills
- Sweating
- Headache
- Fatigue and weakness
- Muscle and joint pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal discomfort
In severe cases:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Anemia (due to destruction of red blood cells)
- Seizures
- Kidney or liver failure
- Confusion or unconsciousness
If any of these symptoms appear, immediate testing and treatment at a certified center like HRTD Medical Institute is crucial.
Treatment After a Positive Malaria Test
Treatment depends on:
- The type of Plasmodium species
- Severity of infection
- Patient’s age and health condition
Common medications include:
- Chloroquine
- Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs)
- Primaquine (for P. vivax and P. ovale)
All medicines should be taken under medical supervision. At HRTD Medical Institute, our doctors ensure that patients receive the right dosage and full course of treatment to prevent relapse and drug resistance.
Complications of Untreated Malaria
Without proper testing and treatment, malaria can lead to:
- Severe anemia
- Cerebral malaria (brain infection)
- Organ failure (kidney, liver)
- Shock and coma
- Death
That’s why testing is the most critical step in managing malaria. At HRTD Medical Institute, our mission is to ensure that no patient suffers due to delayed or inaccurate diagnosis.
Preventing Malaria
While testing and treatment are essential, prevention remains the best defense. Here are some effective preventive measures:
- Use mosquito nets while sleeping.
- Apply mosquito repellents on exposed skin.
- Wear long-sleeved clothing in mosquito-prone areas.
- Keep surroundings clean and avoid stagnant water.
- Spray insecticides regularly at home.
- Take prophylactic medication if traveling to malaria-endemic areas.
HRTD Medical Institute regularly organizes awareness programs to educate communities about mosquito control and malaria prevention.
Role of Diagnostic Centers and Institutes
Institutions like HRTD Medical Institute play a vital role in fighting malaria. Our laboratories are equipped with modern tools and supervised by skilled technologists who ensure accuracy in every test.
We not only perform diagnostic tests but also train students and healthcare professionals in:
- Malaria microscopy
- Blood collection and handling
- Rapid diagnostic techniques
- Result interpretation and reporting
Our goal is to create a future generation of healthcare professionals capable of managing malaria and other infectious diseases effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is malaria contagious?
No. Malaria cannot spread from person to person directly; it spreads only through mosquito bites.
2. How long after a mosquito bite do symptoms appear?
Usually within 7–30 days, depending on the Plasmodium species.
3. Can malaria return after recovery?
Yes. Some species like P. vivax and P. ovale can remain dormant in the liver and cause relapses.
4. Is malaria testing expensive?
At HRTD Medical Institute, malaria tests are affordable and accessible for everyone.
5. Can malaria be cured completely?
Yes, if diagnosed early and treated properly under medical supervision.
Community Awareness and Education
At HRTD Medical Institute, we believe that knowledge saves lives. Our health educators conduct community awareness campaigns to teach people:
- How to recognize early symptoms
- When to seek testing
- How to prevent mosquito breeding
By combining education, testing, and treatment, we aim to reduce malaria cases and improve community health across Bangladesh.
Why Choose HRTD Medical Institute for Malaria Testing
- Accurate and Reliable Tests – Performed by skilled professionals using modern equipment.
- Affordable Services – Accessible to all social groups.
- Fast Results – Rapid turnaround time for both RDT and microscopy.
- Expert Consultation – Doctors available for diagnosis and treatment guidance.
- Educational Opportunities – Training programs for students and laboratory technologists.
- Community Engagement – Awareness programs to prevent malaria outbreaks.
Conclusion
Malaria remains a major public health challenge, but with proper awareness, testing, and prevention, it can be controlled and cured. The malaria test is not just a medical procedure—it is a lifesaving step that protects individuals, families, and entire communities.
At HRTD Medical Institute, we are committed to fighting malaria through accurate diagnosis, quality healthcare, and continuous public education. Our goal is to ensure that every patient receives prompt attention, precise testing, and effective treatment.
Remember, early testing saves lives. If you or someone you know develops fever, chills, or weakness, don’t wait—visit HRTD Medical Institute today for a complete malaria test and professional medical care.
 Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh
Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh