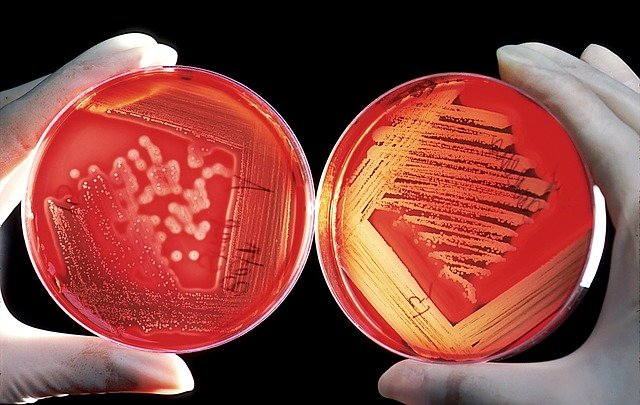
Introduction
Medical science has made remarkable progress in diagnosing and treating infections. Among the most powerful diagnostic tools is the Culture and Sensitivity (C/S) test. This test plays a central role in identifying harmful microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, and in guiding doctors to choose the most effective antibiotics or antifungal drugs for treatment. Without proper culture and sensitivity testing, treatment can become trial-and-error, leading to prolonged illness, antibiotic resistance, or even life-threatening complications.
Training Center for Culture and Sensitivity Test ( C/S Test)
At HRTD Medical Institute, located in Mirpur, Dhaka, we are dedicated to providing advanced training, research, and diagnostic excellence in medical laboratory sciences. Our mission is to empower future healthcare professionals with deep knowledge of laboratory tests such as the C/S test so that they can serve patients with accuracy, responsibility, and compassion.
In this article, we will explore the Culture and Sensitivity test in detail, including its history, purpose, methodology, clinical importance, interpretation, limitations, and future prospects. This comprehensive resource, prepared under the guidance of HRTD Medical Institute, will also serve as an educational reference for students, healthcare providers, and patients alike.
1. What is a Culture and Sensitivity (C/S) Test?
A Culture and Sensitivity test is a microbiological laboratory procedure performed to:
- Culture (Grow) microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi from a clinical specimen (e.g., blood, urine, sputum, pus, throat swab, wound discharge, etc.).
- Identify the exact microorganism responsible for the infection.
- Test Sensitivity to different antibiotics or antifungal agents to determine which drug is most effective for treatment.
This test eliminates guesswork and ensures that patients receive the right drug, at the right dosage, for the right duration.
2. Historical Background of Culture and Sensitivity Test
The roots of microbiological culture go back to the pioneering works of scientists such as Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch in the 19th century. Koch’s development of pure culture techniques laid the foundation for identifying pathogens responsible for diseases like tuberculosis and anthrax. Later, with the advent of antibiotics in the 20th century, the concept of sensitivity testing emerged.
Over time, standardized methods such as the Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Method and automated systems like VITEK revolutionized culture and sensitivity testing. Today, labs like those connected with HRTD Medical Institute combine classical microbiology with modern technology to provide rapid and reliable results.

3. Importance of Culture and Sensitivity Test
The significance of this test can hardly be overstated. Some key reasons include:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Identifies the exact pathogen responsible for infection.
- Targeted Therapy: Prevents the misuse of antibiotics by guiding doctors to the most effective drug.
- Prevention of Resistance: Reduces the development of multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs).
- Cost-effective Care: Prevents unnecessary treatments, reducing hospital stays and patient expenses.
- Public Health Value: Helps in monitoring outbreaks and patterns of antimicrobial resistance.
4. Specimens Used in C/S Testing
Different infections require different types of samples. Commonly used specimens include:
- Urine – For urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Blood – For bloodstream infections or sepsis.
- Sputum – For respiratory infections, e.g., pneumonia, tuberculosis.
- Pus/Wound Swab – For wound or abscess infections.
- Throat/Nasal Swabs – For tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis.
- Stool – For gastrointestinal infections.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) – For meningitis.
At HRTD Medical Institute, students are trained on safe specimen collection and handling techniques, which are critical for obtaining accurate results.
5. Methodology of Culture and Sensitivity Test
The process generally involves several stages:
Step 1: Collection of Sample
- Sterile techniques are crucial to avoid contamination.
- Samples must be transported promptly to the laboratory.
Step 2: Culture Process
- The specimen is inoculated on appropriate culture media (e.g., Blood Agar, MacConkey Agar, Sabouraud Dextrose Agar for fungi).
- Incubation is done at optimal temperature (usually 37°C for bacteria).
- Colonies are observed for growth, shape, color, and other characteristics.
Step 3: Identification of Microorganism
- Microscopic examination (Gram staining, special stains).
- Biochemical tests (e.g., catalase, oxidase, sugar fermentation).
- Automated systems or molecular techniques (PCR, MALDI-TOF).
Step 4: Sensitivity Testing
- Performed using methods like:
- Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Test
- E-test (Epsilometer test)
- Broth dilution methods
- Results classify microorganisms as Sensitive (S), Intermediate (I), or Resistant (R) to different drugs.
6. Clinical Applications of Culture and Sensitivity Test
The Culture and Sensitivity test test is invaluable in managing infections such as:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
- Respiratory Tract Infections (pneumonia, bronchitis)
- Gastrointestinal Infections (bacterial diarrhea, typhoid fever)
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (boils, cellulitis)
- Septicemia and Bacteremia
- Meningitis and Brain Abscesses
- Bone and Joint Infections
By teaching future professionals how to apply these findings, HRTD Medical Institute contributes to better clinical outcomes in Bangladesh and beyond.
7. Interpretation of Results for Culture and Sensitivity Test
- Positive Culture: Indicates presence of infection-causing microbes.
- Negative Culture: Suggests no bacterial or fungal infection (could also mean inadequate sample).
- Sensitivity Report: Lists antibiotics that are effective, guiding treatment plans.
For example, a urine culture may show growth of Escherichia coli, with sensitivity to Nitrofurantoin and resistance to Ciprofloxacin.
8. Limitations of Culture and Sensitivity Test
Despite its importance, the test has limitations:
- Time-consuming (24–72 hours required).
- Prior antibiotic use may give false-negative results.
- Some fastidious organisms are difficult to grow.
- Requires trained personnel and proper infrastructure.
This is why HRTD Medical Institute emphasizes both classical methods and modern rapid diagnostic alternatives in its curriculum.
9. Advances in Culture and Sensitivity Testing
Recent innovations include:
- Automated Culture Systems (faster detection of growth).
- Molecular Diagnostics (PCR, next-generation sequencing).
- Point-of-Care Testing (rapid kits for common infections).
- Artificial Intelligence in Microbiology for faster interpretation.
These advancements are slowly entering Bangladesh, and institutions like HRTD Medical Institute are preparing the next generation of professionals to adapt to these changes.
10. Role of HRTD Medical Institute in Training and Awareness
At HRTD Medical Institute, we provide:
- Lecture Sessions on microbiology and laboratory sciences.
- Practical Training on specimen collection, culture, and sensitivity testing.
- Workshops on infection control and antimicrobial resistance.
- Research Opportunities for students interested in microbiology.
- Community Outreach Programs to educate people about the dangers of antibiotic misuse.
Through this integrated approach, we ensure that graduates not only have technical knowledge but also an ethical responsibility toward patient care.
11. Antibiotic Resistance: A Growing Concern
One of the biggest challenges in healthcare today is antibiotic resistance. Misuse and overuse of antibiotics have led to the rise of “superbugs,” which no longer respond to commonly available drugs.
- WHO has declared antimicrobial resistance (AMR) as one of the top global health threats.
- Bangladesh faces a rising burden of drug-resistant infections due to unregulated antibiotic use.
- The Culture and Sensitivity test is the cornerstone for combating this problem.
At HRTD Medical Institute, we strongly emphasize rational use of antibiotics and the importance of laboratory-based treatment decisions.
12. Patient Awareness and Guidance
For patients, it is important to understand that:
- Self-medicating with antibiotics is dangerous.
- Culture and Sensitivity testing ensures accurate treatment.
- Completing the full antibiotic course is essential, even if symptoms improve.
Healthcare providers trained at HRTD Medical Institute play a key role in patient education.
13. Case Study Example
A 45-year-old man presents with recurrent urinary tract infections. He has been taking antibiotics prescribed by local pharmacies without testing. His infection persists.
After a Culture and Sensitivity test, results reveal growth of E. coli resistant to most common antibiotics but sensitive to Meropenem. The correct treatment is given, and his condition improves.
This case highlights how the Culture and Sensitivity test can save lives.
14. Future Prospects in C/S Testing
The future holds exciting developments:
- Nanotechnology-based rapid tests for instant results.
- AI-driven microbial identification.
- Personalized medicine through genetic profiling of infections.
- Integration with electronic health records for better monitoring.
At HRTD Medical Institute, we prepare students to embrace these future technologies while maintaining strong foundations in classical microbiology.
Conclusion
The Culture and Sensitivity test is one of the most powerful diagnostic tools in modern medicine. It bridges the gap between microbiology and clinical treatment, ensuring patients receive the correct therapy while minimizing the risk of resistance.
At HRTD Medical Institute, we believe that mastering this test is not only a technical skill but also a responsibility toward society. By training skilled professionals, conducting awareness programs, and promoting evidence-based practice, we contribute to building a healthier Bangladesh and a safer world.
Infections may come and go, but the need for accurate diagnosis and rational treatment remains constant. The Culture and Sensitivity test, backed by knowledge and training from HRTD Medical Institute, will continue to guide healthcare providers in this noble mission.
 Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh
Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh