Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Introduction
Pathology is one of the most essential branches of medical science. It connects clinical practice with laboratory diagnosis, making it a cornerstone of modern healthcare. As the healthcare sector in Bangladesh continues to expand, the demand for skilled laboratory professionals — particularly in pathology — is rising rapidly. Hospitals, diagnostic centers, research labs, and medical colleges require well-trained technologists who can perform tests accurately, operate modern equipment, and ensure diagnostic reliability.

Mirpur, one of the fastest-growing educational hubs in Dhaka, is at the center of this transformation. The area is home to thousands of students seeking career-oriented training programs that lead to professional stability and recognition. Among the various training institutions in Mirpur, HRTD Medical Institute stands out as one of the most reputable, modern, and academically advanced institutes offering the Best Pathology Course in Mirpur.
This comprehensive 4,000-word content explains why HRTD Medical Institute is the ideal choice for students wishing to build a strong foundation in pathology. You will learn about the course curriculum, teaching approach, lab facilities, hands-on practice, faculty expertise, admission requirements, career opportunities, and more.

Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 1: Understanding the Importance of Pathology
Pathology is the study of diseases — their nature, causes, development, and effects on the human body. Without pathology, modern diagnostics would not exist. Every time a doctor prescribes a blood test, urine test, biopsy, or any laboratory investigation, the result depends on knowledge derived from pathology.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
1.1 Why Pathology is Vital in Healthcare
Pathology forms the backbone of clinical decisions. Nearly 70% of medical decisions rely on laboratory test results. A skilled pathology technologist can:
- Detect early signs of disease
- Analyze blood, urine, stool, and sputum
- Identify infections, organ dysfunction, metabolic disorders
- Assist in diagnosing cancer, diabetes, infections, autoimmune diseases, and more
1.2 The Need for Skilled Technologists in Bangladesh
Bangladesh’s healthcare sector has grown tremendously over the last decade. Thousands of new diagnostic centers and hospitals have opened, creating a high demand for trained pathology lab professionals. Skilled technologists are needed to maintain quality standards, ensure testing accuracy, operate advanced machines, and follow biosafety protocols.
1.3 Why Students Prefer Pathology as a Career
Students choose pathology because:
- It provides quick employment
- It requires affordable training
- It offers stable and respectable career options
- It provides opportunities to work in hospitals, diagnostics, and research labs
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 2: Pathology Education in Mirpur — An Overview
Mirpur has grown into a major educational hub in Dhaka, hosting colleges, universities, coaching centers, and technical institutes. Within this environment, medical technology training programs — especially pathology — are highly sought after because they offer practical job opportunities.
2.1 Rising Popularity of Pathology Training in Mirpur
Reasons for its popularity include:
- Easy access to healthcare facilities
- Growing number of diagnostic centers
- Higher awareness of medical technology careers
- Affordable and practical study options
2.2 Challenges Students Face in Choosing a Quality Institute
Despite the availability of many institutions, not all provide quality training. Students often face issues like:
- Lack of standard laboratory facilities
- Outdated curriculum
- Insufficient hands-on training
- Unqualified instructors
- No internship or job placement support
This is where HRTD Medical Institute brings a major difference.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 3: Introducing HRTD Medical Institute — The Leader in Pathology Training
HRTD Medical Institute is one of the most trusted and academically advanced institutions in Mirpur for pathology training.
3.1 Location & Accessibility
Address: Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Section-6, Block-Kha, Road-1, Plot-11, Metro Rail Pillar-249, Folpotti Mosque Lane, Mirpur-10, Dhaka-1216
Contact: 01797522136, 01987073965, 01784572173
Located near Mirpur-10 Metro Rail, the institute is easily accessible for students from all over Dhaka.
3.2 Mission & Vision
HRTD Medical Institute aims to:
- Provide internationally standard medical technology training
- Empower students with practical knowledge
- Produce skilled medical technologists who contribute to Bangladesh’s healthcare sector
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
3.3 Why HRTD Medical Institute Stands Out
The institution is known for:
- Modern laboratory setup
- Highly experienced faculty
- Research-based teaching
- Strong monitoring and assessment
- Professional environment
- Affordable tuition fees
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 4: The Best Pathology Course in Mirpur — Detailed Overview
The pathology course at HRTD Medical Institute is specially designed to match both local and international diagnostic standards.
4.1 Course Objective
The main goal of the program is to train students in:
- Clinical pathology
- Hematology
- Biochemistry
- Microbiology
- Immunology
- Lab safety
- Machine operation
- Sample collection and analysis
- Report interpretation
4.2 Who Can Apply
- HSC passed (Science preferred, but not mandatory)
- Students looking for medical technology careers
- Individuals seeking healthcare employment
- Anyone interested in lab-based professions
4.3 Course Duration
The course duration is structured to ensure strong theoretical knowledge as well as extensive hands-on practice.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 6: Some Subjects of the Pathology Course
- Human Anatomy and Physiology
- General Pathology
- Systemic Pathology
- Clinical Pathology
- Microbiology
- General Chemistry for Medical Science
- Biochemistry
- Immunology
- Hematology
- Pathology for Medical Practice
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Some Practical of the Pathology Course
- Blood collection procedure
- Blood grouping
- Cross matching
- Liver function test(SGPT,SGOT)
- kidney function test(serum creatinine, serum urea, Uric acid)
- Lipid profile ( Total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, Triglyceride)
- Urine R/E
- Bleeding time
- Clotting time
- Fasting blood glucose
- Random blood glucose
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- Blood film for CBC test
- Total protein
- ESR
- Serum iron
- Serum Bilirubin
- Hemoglobin
- Thyroid function test (TSH,T3,T4)
- Troponin I
- Vitamin D
- Prolactin hormone
- Dengue NS1
- Dengue IgG and IgM
- Widal test for typhoid fever
- Kala jor
- Chikungunya test
- Malaria
- Prostate specific antigen (PSA)
- Calcium
- CRP
- VDRL
- HBS-Ag
- Anti HCV
- Anti HIV
- ASO
- RA
- Anti H pylori
- Manteaux test
- IgE and many other test
Chapter 6: Teaching Methodology at HRTD Medical Institute
6.1 Theory + Practical Approach
Students spend equal time in classroom learning and laboratory practice.
6.2 Hands-On Training
Every student gets the opportunity to:
- Operate machines
- Perform tests independently
- Work with real samples
- Prepare slides
6.3 Case-Based Learning
Doctors and technologists present real clinical cases to enhance understanding.
6.4 Continuous Assessment
- Weekly tests
- Monthly evaluations
- Lab performance grading
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
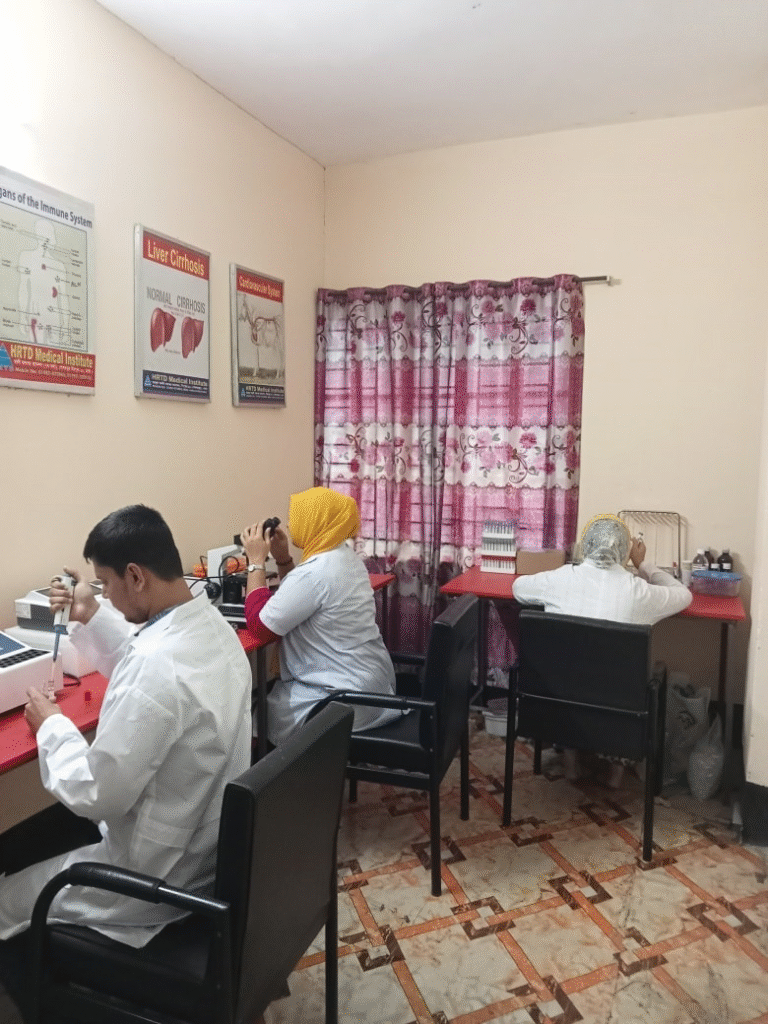
Chapter 7: Laboratory Facilities — A Major Strength of HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute offers one of the most advanced pathology labs in Mirpur.
7.1 Fully Equipped Diagnostic Lab
The lab includes:
- Hematology analyzer
- Biochemistry analyzer
- ELISA reader
- Incubator
- Autoclave
- Microscope sets
- Centrifuge
- Culture media
7.2 Simulated Diagnostic Environment
Students work in a lab setup similar to professional diagnostic centers.
7.3 Safe & Organized Workspace
The institute ensures:
- Clean environment
- Biosafety protocols
- Sterile equipment
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 8: Experienced & Dedicated Faculty Team
8.1 Highly Qualified Instructors
The faculty includes:
- MBBS doctors
- Experienced medical technologists
- Biochemists
- Microbiologists
8.2 Mentoring & Guidance
Teachers provide:
- One-on-one support
- Extra lab practice
- Career counseling
8.3 Guest Lectures
Occasional lectures from pathologists and specialists enhance student exposure.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 9: Internship & Job Placement Opportunities
9.1 Internship Program
The institute arranges internships at:
- Renowned diagnostic centers
- Hospitals
- Private clinics
9.2 Job Placement Support
Students receive help with:
- CV writing
- Interview preparation
- Career planning
9.3 Employment Areas
Graduates can work in:
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic centers
- Blood banks
- Research labs
- NGOs
- Pharmaceutical companies
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 10: Why HRTD Medical Institute Offers the Best Pathology Course in Mirpur
10.1 Top Reasons
- Standard curriculum
- Practical-based learning
- Professional lab environment
- Experienced teachers
- Affordable fees
- Convenient location
- Internship opportunities
- Strong academic support
10.2 Comparison with Other Institutes
While other institutes may provide basic training, HRTD Medical Institute ensures:
- High-quality lab practice
- Modern equipment
- Personalized attention
- Real diagnostic experience
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 11: Student Experience & Learning Environment
11.1 Supportive Academic Atmosphere
Students benefit from:
- Friendly teachers
- Interactive classes
- Regular feedback
11.2 Discipline & Professionalism
The institute maintains:
- Strict attendance rules
- Professional lab discipline
- Safety-focused environment
Chapter 12: Admission Requirements & Process
12.1 Eligibility
- Minimum SSC or HSC pass
12.2 Admission Steps
- Collect admission form
- Submit documents
- Pay registration fee
- Attend orientation
12.3 Required Documents
- Photographs
- NID/Birth certificate
- Previous academic certificates
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 13: Fees & Scholarships
HRTD Medical Institute offers affordable course fees compared to other institutions in Dhaka.
13.1 Flexible Payment Options
Students can pay:
- Monthly
- Semester-wise
- Full payment with discount
13.2 Scholarships
Merit-based scholarships may be available.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 14: Career Growth & Future Prospects
14.1 Local and International Scope
Pathology technologists can work abroad, especially in:
- Gulf countries
- Malaysia
- Singapore
14.2 Higher Study Opportunities
Students can pursue:
- Diploma in Medical Technology
- B.Sc. in Laboratory Technology
- Specialized certifications
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Chapter 15: Final Overview — Why Choose HRTD Medical Institute
HRTD Medical Institute is the ideal choice because it ensures:
- Strong academic foundation
- High-quality lab practice
- Professional training
- Job readiness
Conclusion
The demand for skilled pathology technologists in Bangladesh is rising rapidly, and the need for quality institutions is greater than ever. For students in Mirpur and surrounding areas, HRTD Medical Institute provides the Best Pathology Course in Mirpur with modern facilities, experienced teachers, a strong academic structure, and extensive hands-on training.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Human Anatomy and Physiology
Human Anatomy:
View all
Human anatomy is the scientific study of the structure of the human body, divided into gross anatomy (visible structures like organs) and microscopic anatomy (tissues, cells, etc.). It explores body parts and their organization, crucial for medicine, and involves methods like dissection, imaging (MRI, X-ray), and studying systems (skeletal, muscular, nervous) and regions, focusing on how form dictates function, linking anatomy with physiology.
Key Areas of Study
- Gross Anatomy: Study of structures visible to the naked eye, including organs, bones, muscles, and systems (e.g., circulatory, digestive).
- Microscopic Anatomy: Involves histology (tissues) and cytology (cells) using microscopes.
- Regional Anatomy: Focuses on specific body areas (e.g., head, thorax).
- Systemic Anatomy: Studies the body by organ systems (e.g., nervous, skeletal).
- Clinical Anatomy: Application of anatomical knowledge to medical practice.
Levels of Organization
The body is organized from simple to complex:
- Cells: Basic units of life (e.g., neurons, muscle cells).
- Tissues: Groups of similar cells (e.g., muscle tissue, nervous tissue).
- Organs: Structures made of different tissues working together (e.g., heart, liver, brain).
- Organ Systems: Groups of organs working together (e.g., respiratory, cardiovascular).
Methods of Exploration
- Dissection: Traditional method involving cutting up organisms.
- Medical Imaging: Modern non-invasive techniques like MRI, CT scans, and X-rays for internal views.
- Observation & Palpation: Studying structures on the body’s surface.
Example: Anatomy & Physiology Connection
- Hand: The shape and mobility (anatomy) of the fingers allow for grasping (physiology).
- Muscles: The arrangement of muscle fibers (anatomy) determines how much they can contract (physiology).
Understanding anatomy is fundamental to understanding how the body functions, as structure dictates function.
Human Physiology:
Human physiology is the science of how the human body works, studying its mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions, from cells to organ systems, to maintain a stable internal environment (homeostasis) and respond to challenges like exercise, stress, or disease. It examines systems like nervous, circulatory, respiratory, and digestive, understanding how they interact to keep the body alive and healthy, forming the basis for modern medicine and performance science.
Core Concepts
- Homeostasis: The body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions (like temperature, pH, blood sugar) despite external changes.
- Levels of Organization: From molecules and cells to tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism.
- Interconnected Systems: Organ systems (e.g., nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory) work together, often coordinated by the neuroendocrine system, to achieve body functions.
Key Systems Studied
- Nervous System: Control center, processing signals, thoughts, movements (neurons).
- Endocrine System: Uses hormones to regulate body processes like blood pressure, growth.
- Cardiovascular/Circulatory System: Heart, blood vessels; transports oxygen, nutrients, waste.
- Respiratory System: Lungs, airways; gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out).
- Digestive System: Converts food into fuel, absorbing nutrients.
- Urinary System/Renal: Kidneys; maintain blood volume, filter waste.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
General Pathology
General Pathology studies the fundamental mechanisms of disease, focusing on how cells, tissues, and organs respond to injury, leading to structural and functional changes, and involves diagnosing illnesses through lab tests like biopsies, blood analysis, and advanced imaging to understand the “why” and “how” of disease for patient care. It covers basic cellular responses (inflammation, adaptation, repair) and broad disease processes (infections, cancers) before branching into specific areas like surgical or molecular pathology, acting as a bridge between basic science and clinical medicine.
Core Concepts
- Cellular Injury & Adaptation: How cells cope with stress (e.g., hypertrophy, atrophy, metaplasia) or die (necrosis).
- Inflammation & Repair: The body’s response to damage, including blood vessel changes (hyperemia) and wound healing.
- Disorders of Growth: Neoplasia (cancer) and other abnormal cell proliferation (hyperplasia).
- Biochemical Disturbances: Fatty changes (steatosis) or glycogen accumulation in tissues.
- Infectious Diseases: How pathogens like viruses (HPV causing warts) or parasites (tapeworms causing cysticercosis) cause illness.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Systemic Pathology
Systemic pathology examines specific diseases, causes, mechanisms, and functional changes within individual organs and organ systems (e.g., cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal), contrasting with general pathology’s focus on basic cellular responses. It integrates general pathology principles with clinical manifestations of diseases.
Key aspects of systemic pathology
- Focus: Studies diseases affecting specific organ systems like the heart, liver, kidney, nervous system, skin, etc..
- Content: Covers etiology (causes), pathogenesis (development), morphological appearance (gross and microscopic changes), and clinical effects (signs/symptoms) of diseases in these systems.
- Role: Acts as a bridge between theoretical knowledge (general pathology) and practical medicine, integrating basic science with clinical practice.
- Examples of systems covered: Hematology (blood, bone marrow), Respiratory, Gastrointestinal, Endocrine, Male/Female Reproductive, etc..
Systemic vs. General Pathology
| Feature | General Pathology | Systemic Pathology |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Basic reactions of cells/tissues to injury (inflammation, degeneration, tumors). | Specific responses/diseases of specialized organs/tissues. |
| Level | Broad, fundamental cellular processes. | Organ-specific diseases and manifestations. |
| Application | Universal concepts of disease. | Clinical integration of disease processes. |
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Clinical Pathology
Clinical pathology, also known as laboratory medicine, diagnoses diseases by analyzing bodily fluids (blood, urine, spinal fluid) and tissues using chemistry, microbiology, hematology, and molecular techniques, acting as a vital link between lab tests and patient care to guide treatment. Clinical pathologists oversee these labs, ensuring quality and interpreting results to help doctors manage patient health, covering areas from basic blood counts to complex genetic testing.
Key Aspects of Clinical Pathology
- Tests Samples: Analyzes blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, joint fluid, bone marrow, and other specimens.
- Broad Disciplines: Includes clinical chemistry, hematology (blood disorders), clinical immunology, and molecular pathology.
- Supports Diagnosis: Provides data for diagnosing, monitoring, and preventing diseases, impacting many healthcare decisions.
- Laboratory Focus: Different from anatomic pathology (which examines tissues/organs directly), clinical pathology focuses on the biochemical and cellular components within fluids.
- Professional Role: Involves medical doctors (pathologists) and scientists who manage testing, quality control, and interpret complex results, working with physicians.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Microbiology
Microbiology is the scientific study of microscopic organisms (microbes) like bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea, and protozoa, exploring their structure, function, ecology, and evolution, crucial for understanding disease (pathogens), public health, food production, and biotechnology. This field uses techniques like culturing and molecular methods (PCR) to identify microbes, develop treatments (antibiotics, vaccines), and exploit beneficial microbes, playing a vital role in medicine (infectious diseases), environmental science, and industry.
Key Areas & Organisms
- Bacteria & Archaea: Single-celled prokaryotes, fundamental to life, soil health, and human gut.
- Viruses: Acellular infectious agents that hijack host cells (e.g., flu, SARS-CoV-2).
- Fungi: Yeasts and molds, important in food (bread, beer) and medicine (penicillin).
- Protozoa & Algae: Diverse single-celled eukaryotes, some causing diseases like malaria, others crucial in aquatic food webs.
Importance & Applications
- Healthcare: Diagnosing infections (MRSA, norovirus), developing antibiotics (penicillin), and creating vaccines (smallpox, COVID-19).
- Public Health: Infection control, sanitation, and understanding pandemics.
- Food & Industry: Fermentation (cheese, yogurt), food safety, probiotics, and genetic engineering.
- Environment: Nutrient cycles in soil and water, bioremediation.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
General Chemistry for Medical Science
General Chemistry for Medical Science is the foundational study of chemical principles (atomic structure, bonding, acids/bases, thermodynamics, kinetics) essential for understanding biological systems, pharmacology, and clinical practice, often leading into organic chemistry and biochemistry. It is a core pre-medical prerequisite for most medical schools.
Key topics covered
- Fundamental principles: Stoichiometry, states of matter, atomic/molecular structure, intermolecular forces, solutions.
- Chemical reactions & equilibrium: Kinetics, thermodynamics, chemical equilibrium, acids/bases, buffers, electrochemistry.
- Biological applications: Chemistry of body fluids (pH, blood gas), basic organic/inorganic components, nucleotides (DNA/RNA), coordination compounds.
- Laboratory skills: Titration, solution preparation, safety protocols (PPE, fire, radiation).
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Biochemistry
Biochemistry is the study of chemical processes and substances within living organisms, focusing on life at the molecular level, exploring biomolecules (like proteins, DNA, lipids, carbs) and the reactions that sustain life, energy use, and disease. It blends biology and chemistry, investigating how cells function, communicate, and respond to stimuli, forming the foundation for medicine, genetics, agriculture, and biotechnology by explaining the molecular basis of biological functions and malfunctions.
Core Concepts
- Biomolecules: Understanding the structure, function, and interactions of essential molecules like proteins (enzymes), nucleic acids (DNA/RNA), carbohydrates, and lipids.
- Metabolism: The network of chemical reactions (anabolic/building and catabolic/breaking down) that convert food into energy and cellular components, orchestrated by enzymes.
- Molecular Mechanisms: How genes are expressed, cells communicate, and how these processes are regulated.
Key Areas & Applications
- Medicine: Explaining disease causes (e.g., genetic mutations), drug action, and developing treatments.
- Genetics: The chemical basis of heredity, including DNA structure and function.
- Nutrition: How organisms obtain and use nutrients for survival.
- Biotechnology & Agriculture: Developing new bio-based solutions and improving crops.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Immunology
Immunology is the branch of biology and medicine studying the immune system, the body’s defense network against pathogens (like germs) and abnormal cells, encompassing innate (general) and adaptive (specific, antibody-based) immunity, and how its failures lead to allergies, autoimmune diseases, or cancer, with applications in vaccines, transplants, and new therapies like immunotherapy.
Core Concepts
- Immune System: A complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that identify and fight invaders (antigens).
- Innate Immunity: The body’s first, non-specific defense against general threats.
- Adaptive Immunity: Specific, memory-based immunity involving B cells (producing antibodies) and T cells, which target particular pathogens.
- Antigens: Foreign substances (like bacteria, viruses) that trigger an immune response.
Key Areas of Study & Application
- Vaccinology: Using weakened or inactive pathogens to train the immune system to build defenses.
- Autoimmunity: When the immune system mistakenly attacks the body (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus).
- Allergies: Overreactions to harmless substances (allergens).
- Immunodeficiency: Weakened immune systems, increasing infection risk.
- Transplantation Immunology: Managing immune rejection of foreign organs.
- Cancer Immunology: Using the immune system (like CAR T-cells) to fight tumors (immunotherapy).
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Hematology
Hematology is the branch of medicine focused on studying blood, blood-forming organs (like bone marrow), and blood disorders, covering diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of conditions affecting red cells, white cells, platelets, and clotting factors, including anemias, cancers (leukemia, lymphoma), and bleeding disorders. Hematologists are specialists who diagnose and manage these complex diseases, often alongside oncology.
What Hematology Studies
- Blood Components: Red blood cells (oxygen), white blood cells (immune system), platelets (clotting), and plasma.
- Blood-Forming Organs: Bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, thymus.
- Blood Production (Hematopoiesis): How blood cells are made in the bone marrow.
- Related Systems: Lymphatic and vascular systems, and clotting (hemostasis).
Common Blood Disorders Managed by Hematologists
- Anemia: Lack of healthy red blood cells (e.g., iron deficiency, sickle cell).
- Cancers: Leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma.
- Bleeding/Clotting Disorders: Hemophilia, thrombosis (excessive clotting).
- Hemoglobinopathies: Genetic disorders affecting hemoglobin (e.g., Thalassemia).
What Hematologists Do
- Diagnose conditions through blood tests and biopsies.
- Provide treatments like chemotherapy, immunotherapy, transfusions, or targeted therapies.
- Often work closely with oncologists (hematology-oncology).
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Pathology for Medical Practice
Pathology for Medical Practice is the study of disease causes and effects, essential for diagnosis, treatment planning, disease monitoring, and research, involving the examination of tissues, fluids, and cells to guide clinical decisions. It bridges science and medicine, impacting over 70% of healthcare decisions, from cancer diagnosis to chronic disease management.
Key Aspects of Pathology in Medical Practice
- Diagnostic Role: Pathologists diagnose diseases (e.g., cancer, infections) by analyzing biopsies, blood, urine, and other samples.
- Treatment Guidance: Provides crucial information (tumor type, stage) to oncologists and surgeons for personalized treatment plans (chemo, surgery, etc.).
- Monitoring & Prevention: Tracks chronic disease progression (e.g., diabetes) and identifies early disease potential.
- Forensic/Autopsy: Determines cause of death in suspicious or unknown cases.
Types of Pathology Practices
- Anatomic Pathology: Examines tissues/cells via microscopy (biopsy, cytology, autopsies).
- Clinical Pathology: Analyzes bodily fluids (blood, urine, CSF) using chemistry, microbiology, hematology, and immunology.
- Molecular Pathology: Studies genetic and molecular changes (DNA, proteins) for personalized medicine and cancer diagnostics.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Blood collection procedure
A blood collection procedure, usually venipuncture, involves preparing the patient, applying a tourniquet, selecting and cleaning a vein (often in the inner elbow), inserting a needle at a shallow angle (around 30°), collecting blood into tubes (releasing the tourniquet first), and applying pressure to the site afterward with gauze until bleeding stops, all while maintaining sterile technique and proper labeling.
Key Steps for Venipuncture (Most Common Method)
- Preparation & Patient ID:
- Verify patient and test info, perform hand hygiene, and explain the process.
- Have the patient sit or lie down comfortably, with the arm supported below heart level.
- Equipment & Site Selection:
- Gather necessary sterile equipment (needle, tubes, tourniquet, antiseptic, gauze).
- Apply the tourniquet 4-5 finger-widths above the chosen site (inner arm bend) and ask the patient to make a fist.
- Palpate (feel) for a strong, bouncy vein; don’t re-touch the area after cleaning.
- Puncture & Collection:
- Clean the site with 70% isopropyl alcohol and let it air dry completely.
- Anchor the vein by pulling skin taut below the site with your thumb.
- With the needle’s bevel (opening) facing up, insert it swiftly into the vein at a 15-30° angle.
- Once blood flows, release the tourniquet (before two minutes) and slowly pull back the syringe plunger or push the vacutainer tube onto the needle.
- Fill tubes in the correct order, inverting them gently to mix if needed (e.g., EDTA tubes).
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Blood grouping
Blood grouping classifies blood into types (A, B, AB, O) based on specific antigens (proteins) on red blood cells and antibodies in plasma, combined with the presence or absence of the Rh factor, creating eight main groups (A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, AB-) crucial for safe blood transfusions, as receiving incompatible blood can be fatal. O negative is the universal donor, and AB positive is the universal recipient, due to their lack of A/B antigens or antibodies, respectively, allowing them to mix with most other types.
The ABO System (Antigens & Antibodies)
- Blood Group A: Has A antigens on red cells, anti-B antibodies in plasma.
- Blood Group B: Has B antigens on red cells, anti-A antibodies in plasma.
- Blood Group AB: Has both A and B antigens, but no antibodies.
- Blood Group O: Has neither A nor B antigens, but both anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
The Rh Factor (Positive/Negative)
- Rh Positive (+): Has the Rh protein (D antigen) on red blood cells.
- Rh Negative (-): Lacks the Rh protein.
Compatibility & Transfusions
- Universal Donor: O Negative (O-) can donate to anyone because it lacks A, B, and Rh antigens, so recipients don’t form antibodies against it.
- Universal Recipient: AB Positive (AB+) can receive from anyone because it has A, B, and Rh antigens, meaning it already has antibodies for those types.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Liver function test
A Liver Function Test (LFT) is a panel of blood tests measuring enzymes, proteins, and substances like ALT, AST, ALP, GGT, bilirubin, and albumin to assess liver health, detect damage or disease (like hepatitis, cirrhosis, or blockages), monitor treatment effectiveness, and check for medication side effects, providing a comprehensive view of how well the liver is working by checking levels of these liver-produced or liver-related chemicals.
What it checks
- Liver Enzymes (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT): Elevated levels often signal liver cell damage or inflammation, with specific patterns suggesting different issues (e.g., GGT helps differentiate liver/bone issues).
- Bilirubin: A yellow pigment; high levels can indicate liver disease or bile duct blockage.
- Albumin & Total Protein: Measures the liver’s ability to produce proteins crucial for bodily functions.
- Prothrombin Time (PT/INR): Checks how quickly blood clots, as the liver produces clotting factors; prolonged time suggests impaired function.
Why it’s done
- Screening: To check for liver disease in at-risk individuals (heavy drinkers, obese, diabetic).
- Diagnosis: To find the cause of symptoms like jaundice, abdominal pain, or fatigue.
- Monitoring: To track the progression of liver disease or treatment response.
- Medication Safety: To ensure certain drugs aren’t harming the liver.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
kidney function test
A kidney function test (KFT) uses blood and urine tests to check how well your kidneys filter waste, balancing fluids and minerals. Key blood tests measure waste products like Creatinine (used to calculate eGFR), Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), and electrolytes, while urine tests look for protein or glucose. These help diagnose kidney disease, monitor existing conditions (like diabetes/high BP), or check medication effects, with imaging (ultrasound) or biopsy used for deeper investigation.
Common Blood Tests
- Creatinine: A waste product from muscle breakdown; high levels suggest poor filtering.
- eGFR (Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate): Calculated from creatinine, age, sex, etc., showing overall kidney filtering efficiency (higher is better).
- BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen): Measures urea, another waste product; elevated levels can signal kidney issues.
- Electrolytes: Sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate levels help check fluid balance.
Common Urine Tests
- Urinalysis: Checks for protein (albumin), glucose, blood, and other signs of damage.
- Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (ACR): Detects small amounts of albumin, an early sign of damage.
Pathology Course in Mirpur 01797522136
Lipid profile
A lipid profile is a blood test that measures fats (lipids) in your blood, including total cholesterol, “good” HDL, “bad” LDL, VLDL, and triglycerides, to assess your risk of cardiovascular disease (heart attack, stroke) by checking for plaque buildup in arteries. It helps doctors monitor heart health, guide lifestyle changes, and manage conditions like high cholesterol, often requiring a 9-12 hour fast beforehand for accurate results.
Key components measured:
- Total Cholesterol: All cholesterol in your blood.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): “Bad” cholesterol that can clog arteries.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): “Good” cholesterol that removes LDL from your body.
- Triglycerides: A type of fat from food, used for energy; high levels increase heart risk.
- VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein): Transports triglycerides and can also build up in vessels.
Purpose of the test:
- Assess Risk: Determine your risk for heart disease, stroke, and atherosclerosis (plaque buildup).
- Monitor Treatment: Check if diets or medications are effectively lowering cholesterol.
- Screening: Often done during routine physicals to catch issues early, as high lipids often have no symptoms.
Urine R/E
“Urine re” usually refers to a Urine Routine Examination (RE), also called Urinalysis, a common test checking urine’s appearance, concentration, and content (physical, chemical, microscopic) for UTIs, kidney/liver disease, diabetes, or general health, often paired with a CS (Culture & Sensitivity) for infection-causing microbes. It involves checking color, pH, specific gravity, and looking for cells, bacteria, or crystals, helping diagnose issues like kidney stones, infections, or metabolic disorders.
What it checks (RE/ME)
- Routine Examination (RE): Physical & Chemical aspects (Color, clarity, pH, protein, glucose, etc.).
- Microscopic Examination (ME): Microscopic view for Red/White Blood Cells, bacteria, crystals, casts.
- Culture & Sensitivity (CS): Grows bacteria to identify the specific microbe and best antibiotic.
Why it’s done
- Routine check-ups: General health screening.
- Symptom investigation: Painful urination, blood in urine, abdominal/back pain.
- Diagnosis: Kidney disease, diabetes, liver disease, UTIs, kidney stones.
- Monitoring: Tracking disease progression or pre-surgery.
How to give a sample (Mid-Stream Urine – MSU)
- Wash genitals thoroughly.
- Start urinating into the toilet.
- Collect 10-20 ml of the mid-stream (middle part) urine in a sterile container.
- Send to the lab quickly or refrigerate for a short time.
Bleeding time
Bleeding time (BT) is a medical test measuring how long it takes for a small skin cut to stop bleeding, assessing primary hemostasis (platelet plug formation) and vessel function, with normal times generally 3-10 minutes, though it’s less common now due to poor specificity. Prolonged times suggest platelet issues (like low count or poor function), vascular problems, or certain meds (aspirin) and can indicate conditions like thrombocytopenia, Von Willebrand disease, or liver disease, while shortened times usually aren’t significant.
How it’s Performed (Ivy Method Example)
- A blood pressure cuff is inflated on the upper arm to maintain steady pressure.
- Two small, shallow cuts are made on the forearm.
- The cuff is deflated.
- Filter paper blotted to the cuts every 30 seconds until bleeding stops.
- The total time is recorded.
What it Shows
- Normal: 3 to 10 minutes (varies by method).
- Prolonged: Suggests issues with platelet function, platelet count (e.g., thrombocytopenia), blood vessel integrity, or medications like aspirin.
- Conditions: Can point to von Willebrand disease, liver disease, or certain blood disorders.
Blood glucose
Blood glucose, or blood sugar, is the main sugar in your blood, your body’s primary energy source from food (especially carbs). It’s regulated by insulin, a hormone that moves glucose into cells; imbalances can signal diabetes (high levels) or hypoglycemia (low levels). Monitoring these levels, often with a meter, helps manage conditions like diabetes and prevents long-term complications by keeping levels in a target range (e.g., fasting <100 mg/dL, 2 hrs post-meal <180 mg/dL).
What it is
- Energy Source: Glucose is your cells’ main fuel, carried in the bloodstream from the food you eat (fruits, bread, pasta).
- Hormonal Control: Insulin (from the pancreas) helps cells absorb glucose; glucagon releases stored glucose when levels are low.
Why it matters
- Diabetes: High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or use it effectively, leading to diabetes.
- Complications: Consistently high glucose damages blood vessels and nerves, increasing risks for heart disease, kidney issues, and eye problems.
Normal vs. High Levels (General Guidelines)
- Fasting (no food for 8+ hrs): Under 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is normal; 100-125 mg/dL is prediabetes; 126 mg/dL+ is diabetes, says the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK).
- 2 Hours After a Meal: Under 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) is a typical target for people with diabetes, notes MedlinePlus.
Total protein
Total protein refers to the overall amount of protein in your blood, a key indicator of health measured by a blood test, combining two main types: albumin (for fluid balance, transport) and globulins (for immune function, transport). Levels help diagnose liver, kidney issues, or malnutrition, indicating if your body makes too much or too little, with abnormal levels often needing further tests like the A/G ratio.
What it measures
- Albumin: The most abundant protein, preventing fluid leaks from vessels and carrying hormones, vitamins, and fats.
- Globulins: A group including antibodies (gamma globulins) for immunity, plus alpha and beta globulins for transport.
Why it’s tested
- To check liver and kidney function.
- To help diagnose malnutrition or nutritional deficiencies.
- To investigate symptoms like swelling, fatigue, or frequent infections.
- To monitor chronic diseases.
ESR
ESR usually stands for Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, a common blood test measuring how fast red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle in a tube, indicating inflammation in the body, often from infections, autoimmune issues, or other conditions. Faster settling (higher ESR) means more inflammation, as cells clump together and get heavier; it helps monitor disease but doesn’t diagnose a specific cause. ESR also refers to the European Society of Radiology, a professional organization for medical imaging.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (Blood Test)
- What it is: A test measuring how quickly red blood cells (RBCs) fall to the bottom of a test tube.
- How it works: Inflammation causes proteins to make RBCs clump, making them heavier and sink faster.
- What it shows: A high ESR signals inflammation, but it’s non-specific, meaning it doesn’t pinpoint the exact disease.
- When it’s used: To detect inflammation from infections, autoimmune diseases (like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), and cancers, and to monitor chronic conditions.
Serum Bilirubin
Serum bilirubin is a blood test measuring a yellow pigment from red blood cell breakdown, crucial for checking liver function, diagnosing jaundice, bile duct issues, or blood disorders like hemolytic anemia, with levels indicating how well the liver processes bilirubin, as high levels can signal disease but also have protective antioxidant roles. The test measures total bilirubin (direct + indirect) and helps doctors see if your liver is healthy or struggling, often alongside other liver tests.
What it is
- Bilirubin: A yellowish substance produced when old red blood cells break down.
- Liver’s Role: A healthy liver processes bilirubin for excretion in bile, but if the liver’s struggling or blocked, bilirubin builds up in the blood.
Why the test is done
- Diagnose Jaundice: Yellow skin/eyes.
- Check Liver Health: Signs of hepatitis, cirrhosis, or drug damage.
- Find Bile Duct Blockages: From gallstones or tumors.
- Monitor Blood Disorders: Conditions where red blood cells break down too fast (like hemolytic anemia).
- Newborn Jaundice: To see if newborns need treatment (phototherapy).
Types of Bilirubin Measured
- Total Bilirubin: Sum of direct and indirect.
- Indirect (Unconjugated): Bilirubin before it’s processed by the liver.
- Direct (Conjugated): Bilirubin after it’s processed by the liver.
What high levels can mean (Hyperbilirubinemia)
- Liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis).
- Bile duct obstruction.
- Excessive red blood cell destruction (hemolysis).
What low levels can mean (Hypobilirubinemia)
- Often not a problem; possibly caffeine or certain medications.
- May be linked to some autoimmune diseases or better cardiovascular health.
Normal Ranges (Adults)
- Total: Roughly 0.1 to 1.2 mg/dL (varies by lab).
- Direct: Around 0.1 to 0.3 mg/dL.
- Indirect: Around 0.2 to 0.8 mg/dL.
Thyroid function test
A thyroid function test (TFT) is a blood test checking Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), T4 (thyroxine), and sometimes T3 (triiodothyronine) levels to see how well your thyroid gland in your neck is working, helping diagnose conditions like hypothyroidism (underactive) or hyperthyroidism (overactive), or to monitor treatment. The TSH test is usually first, with high TSH often signaling an underactive thyroid and low TSH an overactive one, but T4 and T3 levels confirm the diagnosis.
Key Tests Included in a Thyroid Panel:
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): The most common first test, measuring the hormone from the pituitary gland that tells the thyroid to produce hormones. High TSH means the thyroid isn’t making enough (underactive); low TSH means it’s overproducing (overactive).
- Free T4 (Free Thyroxine): Measures the main thyroid hormone circulating in your blood, showing how much the gland is actively producing.
- Free T3 (Free Triiodothyronine): Measures the active form of thyroid hormone; often checked if hyperthyroidism is suspected.
Why It’s Done:
- To diagnose thyroid disorders (hypo/hyperthyroidism).
- To monitor treatment, like hormone replacement therapy.
- To investigate symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, or changes in heart rate.
What to Expect:
- A simple blood draw from a vein in your arm.
How Results Are Interpreted (General Guide):
- Hypothyroidism (Underactive): High TSH, Low Free T4/T3.
- Hyperthyroidism (Overactive): Low TSH, High Free T4/T3.
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism: High TSH, but normal T4/T3 levels.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D, often called the “sunshine vitamin,” is a fat-soluble nutrient crucial for calcium absorption, strong bones, muscle function, and immune health, produced by skin exposure to sunlight but also obtained from fatty fish, fortified foods, and supplements. Deficiency can lead to bone diseases like rickets (children) or osteomalacia (adults), so many people, especially in winter or with low sun exposure, need supplements, while some foods (milk, cereals) are fortified, and sunlight remains a key source.
Key Functions
- Bone Health: Helps absorb calcium and phosphorus for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth, preventing rickets and osteoporosis.
- Immune Support: Supports the immune system to fight infections.
- Muscle & Nerve Function: Essential for muscle movement and nerve communication.
Sources
- Sunlight: Skin produces Vitamin D3 when exposed to UVB rays, but this varies by season, location, skin type, and time of day.
- Foods: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), egg yolks, red meat, liver, and fortified foods like milk, cereals, and plant-based milks.
- Supplements: Available as D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol).
Deficiency & Risk Factors
- Risks: People with dark skin, older adults, those with low sun exposure (due to work, location, clothing), and certain medical conditions.
- Symptoms: Bone pain, weak bones.
Prolactin hormone
Prolactin is a hormone from the pituitary gland essential for breast development and milk production (lactation) in women, but it affects many body functions in both sexes, including reproduction and metabolism. Levels naturally rise during pregnancy, but high levels (hyperprolactinemia) can cause irregular periods, infertility, low libido, erectile dysfunction, and unexpected milk production (galactorrhea). Causes of high prolactin include pituitary tumors (prolactinomas), hypothyroidism, stress, certain medications, and kidney/liver disease, with dopamine (a neurotransmitter) usually inhibiting its release.
Key Functions
- Lactation: Stimulates milk production in new mothers.
- Reproduction: Affects ovarian function in women and testicular function in men, influencing fertility and sexual function.
- Other Roles: Involved in metabolism, immune system regulation, and other bodily processes.
Causes of High Prolactin (Hyperprolactinemia)
- Pituitary Tumors: Benign tumors called prolactinomas.
- Medical Conditions: Hypothyroidism, kidney or liver disease, chest injuries, shingles.
- Medications: Antidepressants, antipsychotics, blood pressure drugs, opioids.
- Physiological: Stress, sleep, exercise, nipple stimulation, eating.
Symptoms of High Prolactin
- In Women: Irregular or absent periods, infertility, low libido, breast milk production outside of pregnancy.
- In Men: Low libido, erectile dysfunction, infertility, breast enlargement (rare).
- In Both: Galactorrhea (milky nipple discharge).
Regulation & Treatment
- Inhibition: Dopamine from the hypothalamus usually keeps prolactin levels low.
- Stimulation: Hormones like estrogen and TRH, as well as stress, can increase levels.
- Treatment: Often involves medications (like bromocriptine) to lower levels, especially for prolactinomas, or addressing underlying causes like hypothyroidism.
 Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh
Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh