Molecular Biology Test
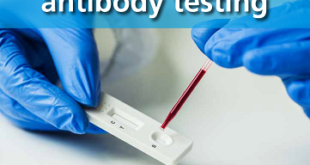
Molecular biology tests are laboratory methods that examine a patient’s DNA, RNA, or proteins to diagnose diseases or conditions. Their advantages include high sensitivity, which can detect diseases at low levels, and efficiency, as they often require small sample volumes and don’t need culturing. Disadvantages include the risk of sample contamination leading to false positives, test inhibition from substances in the sample, and potential issues with sample quality or availability.
Definition
- Molecular testing involves analyzing a sample of tissue, blood, or other body fluid for specific genes, proteins, or other molecules that may indicate a disease or condition.
- This is based on the field of molecular biology, which studies the structure and function of biological molecules and macromolecular systems, particularly the molecular basis of inheritance and protein synthesis.
- A common technique is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), which amplifies small amounts of genetic material for easier detection.
Causes (What they test for)
Molecular tests are used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including:
- Infectious diseases: Identifying the genetic material of viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens.
- Genetic disorders: Detecting specific gene mutations associated with inherited conditions.
- Cancers: Identifying specific mutations in genes that can affect cancer growth and treatment.
Advantages
- High Sensitivity: Can detect organisms or mutations at very low levels that other methods might miss.
- Minimal Sample Volume: Often requires only a small amount of sample, such as a blood or tissue sample.
- No Culture Required: Many tests do not need the organism to be grown in a lab, which can save time.
- High Accuracy: Can provide very accurate results because they measure specific DNA or RNA sequences.
Disadvantages
- Sample Contamination: Even a tiny amount of contamination can lead to a false positive result.
- Test Inhibition: Substances in some samples, particularly those from complex biological sites, can interfere with the test’s reactions.
- Sample Issues: Insufficient sample quality or quantity can hinder the process.
- Limitations with Viability: Some tests can detect non-viable (inactivated) organisms, which pose no threat, making it difficult to distinguish them from active infections based on the test alone.
- Cost and Accessibility: Can be more expensive and less accessible than other testing methods.
 Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh
Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh