ASO Test
Introduction
Medical science has advanced tremendously in the field of diagnostics, allowing doctors to detect and treat diseases at an early stage. Among the many laboratory investigations available today, the ASO Test (Antistreptolysin O Test) plays a crucial role in identifying post-streptococcal infections. This test is widely used to detect complications that can arise after a streptococcal infection, such as rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis.
At the HRTD Medical Institute, Mirpur, Dhaka, we prioritize the importance of diagnostic tests like the ASO test in both clinical training and patient care. Our institution ensures that students, trainees, and healthcare professionals understand not only the theory behind such tests but also the practical skills required to perform them accurately.
This article will provide an in-depth explanation of the ASO test, including its principles, procedures, clinical significance, interpretation, and the importance of training at HRTD Medical Institute for aspiring pathology and medical students.
What is the ASO Test?
The ASO test is a blood test used to measure the level of antistreptolysin O antibodies in the serum. These antibodies are produced by the immune system in response to an infection caused by Group A Streptococcus bacteria.
When the human body is infected by streptococcus bacteria, the bacteria release a toxin called streptolysin O, which can damage red blood cells and tissues. In response, the immune system produces antistreptolysin O (ASO) antibodies to neutralize the toxin. The presence of these antibodies in the blood helps in diagnosing recent or past infections.
Importance of ASO Test
The ASO test is not typically used to diagnose an ongoing streptococcal infection (such as strep throat). Instead, it is most useful in identifying complications that may arise after the infection has subsided.
Some of the major clinical importance of the ASO test includes:
- Diagnosis of Rheumatic Fever
- Rheumatic fever is a serious inflammatory condition that can damage the heart valves. It usually develops 2–4 weeks after an untreated streptococcal throat infection. The ASO test helps confirm the history of streptococcal infection in such cases.
- Diagnosis of Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
- PSGN is a kidney disease that can occur after a streptococcal infection. ASO titers can support the diagnosis by confirming exposure to streptococcus.
- Understanding Past Infections
- A positive ASO test indicates that the patient has had a recent streptococcal infection, even if symptoms were mild or unnoticed.
- Epidemiological Studies
- ASO testing is often used in research and public health to understand the prevalence of streptococcal infections in certain populations.
Principle of ASO Test
The ASO test is based on the principle of antigen-antibody reaction. Streptolysin O is an antigen, and the human immune system produces antibodies (ASO) against it.
There are different methods to perform the test, including:
- Latex Agglutination Method – Quick and commonly used.
- Nephelometry – Measures turbidity caused by antigen-antibody complexes.
- Turbidimetric Method – Quantifies antibody levels.
At HRTD Medical Institute, students are trained in these techniques with practical laboratory exposure to ensure accuracy in results.
Normal Values of ASO Test
- In adults: less than 200 IU/mL
- In children: less than 400 IU/mL
However, normal ranges may vary slightly depending on laboratory standards and geographic location.
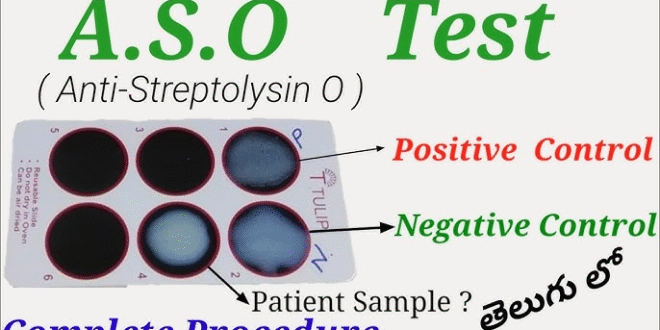
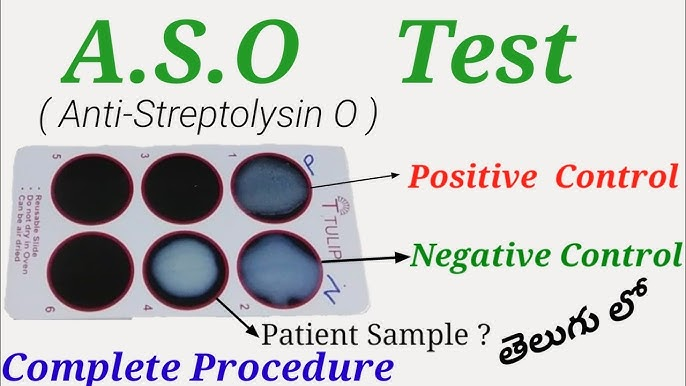
Procedure of ASO Test
Sample Collection
- A blood sample is collected from a vein.
- Serum is separated for analysis.
Testing Process (Latex Agglutination Method)
- Patient serum is mixed with latex particles coated with streptolysin O antigen.
- If antibodies are present, agglutination (clumping) occurs.
- The degree of agglutination is compared with standards to estimate ASO levels.
Precautions
- Hemolyzed or lipemic samples should be avoided.
- The test should not be performed immediately after infection, as antibodies take 1–3 weeks to develop.
Interpretation of Results
- Negative Result: ASO levels are within the normal range, indicating no recent streptococcal infection.
- Positive Result: Elevated ASO levels suggest a recent infection or complications such as rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis.
Note:
A single ASO test may not be conclusive. Doctors often recommend repeating the test or combining it with other investigations like anti-DNase B test for confirmation.
Limitations of ASO Test
- Not all patients with streptococcal infections develop high ASO levels.
- ASO levels may remain elevated for months even after recovery.
- Other tests may be needed for accurate diagnosis.
Clinical Applications of ASO Test
- Cardiology: To detect post-streptococcal complications affecting the heart.
- Nephrology: To diagnose kidney inflammation after streptococcal infection.
- Pediatrics: Children are more prone to streptococcal infections; ASO testing helps in early detection of complications.
- Rheumatology: Helps rule out autoimmune reactions triggered by streptococcus.
ASO Test Training at HRTD Medical Institute
At the HRTD Medical Institute, Mirpur, Dhaka, we provide structured training programs for students in pathology, medical laboratory technology, and diagnostic medicine. Our ASO test training module includes:
- Theoretical Lessons
- Understanding streptococcus bacteria and immune response.
- Role of ASO in post-infectious diseases.
- Practical Demonstration
- Blood sample collection and handling.
- Performing ASO test using different methods (latex agglutination, nephelometry, etc.).
- Hands-On Training
- Students get the opportunity to perform the test themselves under supervision.
- Emphasis on accuracy, interpretation, and error prevention.
- Case-Based Discussions
- Real case studies on rheumatic fever and kidney disease linked with streptococcal infections.
- Assessment and Certification
- Students are evaluated on both theory and practical skills.
- Certification from HRTD Medical Institute enhances career opportunities.
Why Choose HRTD Medical Institute for ASO Test Training?
- Experienced Faculty – Our instructors are skilled in clinical pathology and laboratory diagnostics.
- Modern Laboratory Facilities – Equipped with updated diagnostic tools for hands-on training.
- Comprehensive Curriculum – Covering theory, practice, and case-based learning.
- Career Opportunities – Our certified students find opportunities in hospitals, diagnostic centers, and research labs.
- Location Advantage – Conveniently located at Mirpur-10, Dhaka, easily accessible to students.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What does a high ASO titer mean?
A high ASO titer indicates a recent streptococcal infection and possible complications like rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis.
Q2. Can ASO test detect strep throat?
No, the ASO test is not suitable for detecting acute strep throat. It only shows past infections.
Q3. How long do ASO levels remain elevated?
They may stay elevated for several months after infection.
Q4. Can the ASO test be false positive?
Yes, sometimes due to other conditions or cross-reactivity, results may be misleading.
Q5. Why should students learn ASO testing at HRTD Medical Institute?
Because our training emphasizes both practical laboratory skills and real clinical applications, ensuring that students are industry-ready.
Conclusion
The ASO test is a vital diagnostic tool that helps in identifying the after-effects of streptococcal infections, particularly in detecting rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis. Proper understanding and training in this test are crucial for medical students and healthcare professionals.
At HRTD Medical Institute, we provide world-class education and hands-on laboratory training to ensure students are well-prepared for careers in medical diagnostics. Our focus on tests like ASO ensures that learners not only understand the scientific principles but also gain the confidence to apply them in real-world healthcare settings.
By mastering the ASO test at our institute, students become capable of contributing to accurate disease diagnosis and improving patient outcomes in Bangladesh and beyond.
 Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh
Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh Best Pathology Training Institute in Bangladesh